Pre-cold management of grapes is an important period for the management of the whole year. In order to ensure high yields and stable production of grapes for the following year, it is necessary to strengthen grape management before cold protection. The following tasks must be done: 1. Late management In the late growth period of grape, it is necessary to strictly control the vegetative growth of the tree and promote the differentiation of flower buds, which is the key measure to ensure the production of the following year. Based on strict soil and water management, take control of tipping, remove some dense branches and useless branches, and remove part of the old leaves to control the vegetative growth of the tree, and guard against sprouting of winter buds, so that the plane ventilation and light transmission Branches are substantial. The foliar fertilizer was applied to the tops of the leaves. The main fertilizers were phosphate fertilizer and potash fertilizer. The grapes were sprayed once every 10 to 15 days in advance of harvest and sprayed 2 or 3 times to increase the sugar content of the fruits and increase the yield; 2 to 3 times, to promote the maturity of branches, is conducive to accumulation of nutrients and improve the ability of the tree to withstand cold, can safely winter. 2. Timely cultivator Grapes often encounter rainy weather during the late period of growth and development, resulting in soil compaction. Timely cultivating and weed control can prevent flooding and improve the growth environment of the root system, increase the permeability of the soil, and eliminate weeds in time to reduce pests and diseases. 3. Water and fertilizer management In the management of water, attention should be paid to the fact that the fruit enters the inflated period and is grounded with fine water, and those who have conditions can cover the grass and cover the film in the vineyard, which can not only protect the earthworms but also prevent the fruit cracking caused by the great change in the soil moisture content; In case of heavy rain, it should be drained and flooded in time. Basal fertilizer is the most important part of vineyard fertilization. Basal fertilizer is applied in the autumn and can be carried out after the grapes are harvested and before the soil is frozen. However, production practices have shown that as early as autumn, basal fertilizer is better. The basal fertilizer is usually applied immediately after the grapes are harvested with decomposed organic fertilizer (fertilizer, compost, etc.), because the root system enters a new peak of growth. The basal fertilization roots are easily healed and some new roots can be emitted, and the tree body can be increased. The nutrient reserve is conducive to the sprouting, flowering and early growth of young shoots. Add some quick-acting fertilizers such as ammonium nitrate, urea and superphosphate, and potassium sulfate during fertilization. Basal fertilizer has a good effect on restoring tree vigor, promoting root absorption and flower bud differentiation. There are two methods for applying basal fertilization: the withdrawal of the whole garden and the application of furrows, which can be carried out in combination with the method of deep-turning the soil and improving the strip, ring, or radial furrow. Most of the grapes in the scaffolding are used for spreading, and the fertilizer is then buried with shovels or ploughs. Spreading fertilizers often causes the grape roots to float and should be applied as a ditch or a hole. Ditch grape is often used ditch. The method is to open the ditch 50 cm from the plant, 40 cm wide and 50 cm deep. Apply 25-50 kg of organic fertilizer per mu, 250 kg of superphosphate and 150 kg of urea. A layer of fertilizer fills the ditch in succession with a layer of soil. In order to reduce the workload of fertilization, it is also possible to adopt the method of intercropping and trenching fertilization, that is, digging trenches for fertilization in the first, third and fifth lines in the first year, digging trenches for fertilization in the second, fourth and sixth lines in the second year. , so that the whole garden soil has been deep turned and improved. 4. Pest control The key to pre- and post-harvest grape management is to protect the fruit. This period of pest control should focus on white rot, anthrax, downy mildew and spider mites, leafhoppers, etc., the choice of agents: 50% carbendazim 600 times, or 70% thiophanate-methyl 600 times, Or 78% Cobo 600 times, or 80% spray 600 times, or 1:0.5:200 times Bordeaux mixture, etc., spraying once every 10 to 15 days. At the same time, it is necessary to cut off diseased leaves and fruit in a timely manner. 5. timely harvest Timely harvesting mature fruits not only prevents fruit ripening and affects quality, but also reduces tree nutrient consumption, which is beneficial to sprouting, fruit setting, new shoots, and robust growth of leaves in vertical years. 6. Trim the garden After harvesting the fallen leaves, the grapes should be trimmed and cleaned in time to remove the fruit bags, rotten fruit, fallen leaves, and weeds. Burning or deep burying of these sundries can greatly reduce the number of pathogenic bacteria, laying a good foundation for prevention and control of grape pests the following year.
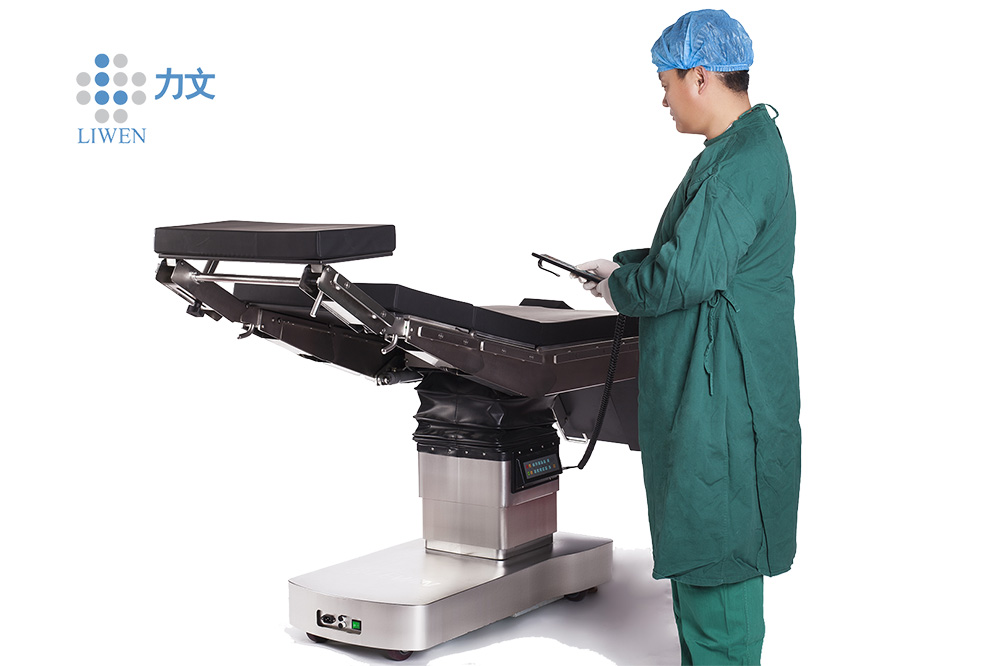
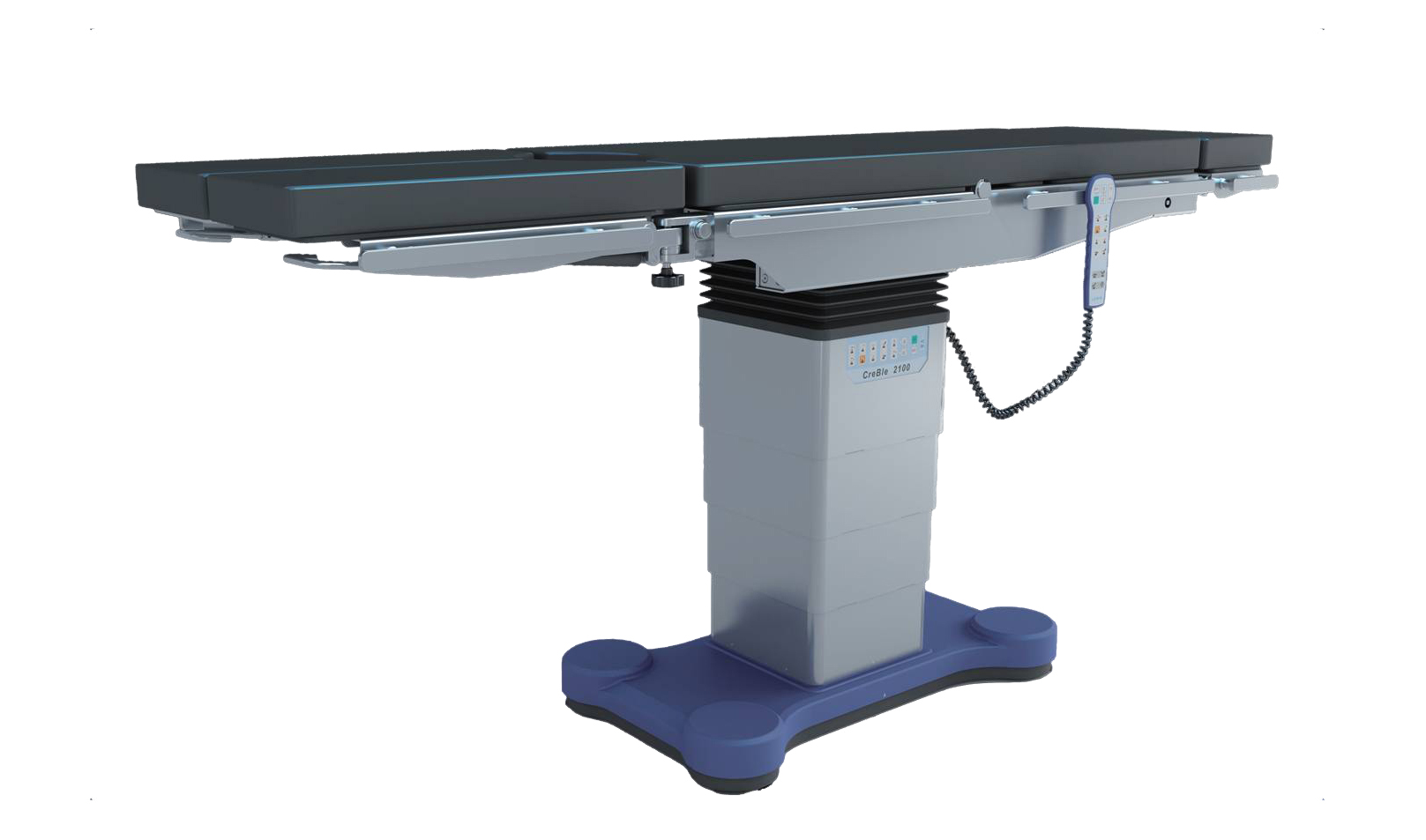
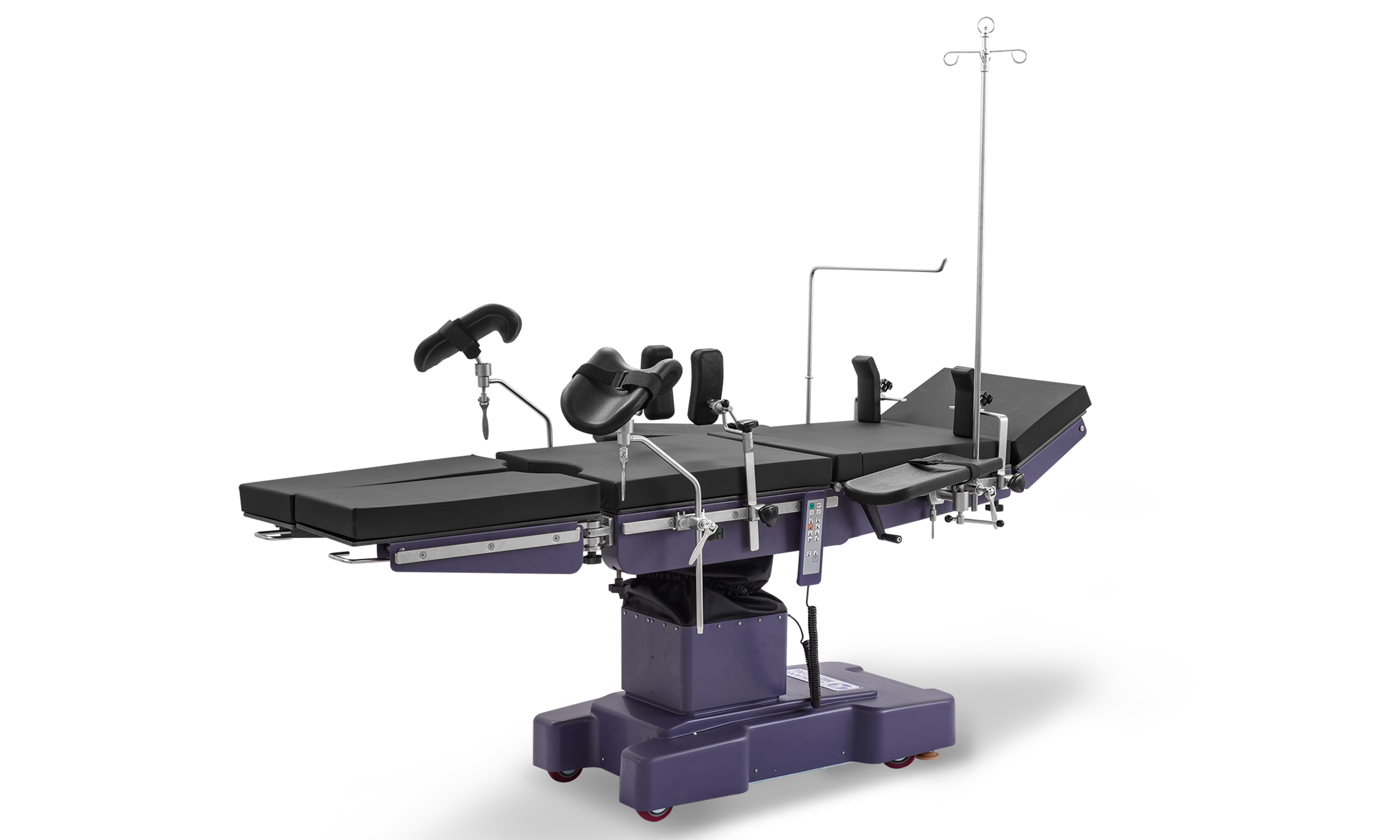
Operating table is used at surgical operation room, our table can use for almost all kinds of surgries; For surgical table, we have three types, electric operation table, electric hydraulic operation table; Manual surgical table; Lewin company do much investment on new products research every year, to research new type surgical table to meet the hospital requirment;we Lewin has High grade surgical table, middle grade surgical table to meet different requirments from user; The OT table adopt imported parts, much stable and safty;
Operating Table,Surgery Table,Surgical Table,Electric Hydraulic Operating Table Shandong Lewin Medical Equipment Co., Ltd. , https://www.lewinmed.com