[Rui Sai Xiao Class] 2015 breakthrough research in the field of cancer TOP10
Ruisai Small Classroom 159
Scientists have spent a lot of time on revealing new ways to develop cancer, develop treatments, and prevent cancer. With the deepening of research and the discovery of multiple mechanisms, scientists have turned cancer into a controlled disease. .
Recently, scientists from the Texas A&M Health Science Center found that extracts from broccoli called sulforaphane may help treat cancer; others have found that meditation can also help cancer treatment; such positive research There are many, and some researchers have found that other components of the body may affect the occurrence of cancer. For example, in a research report published in Science, scientists from France found that intestinal microbes can affect the effectiveness of cancer immunotherapy.
2015 is coming to an end. What breakthroughs have scientists made in the field of cancer in the past year? Xiaobian took stock of the top 10 highlights of 2015.
[1] A drop of blood to diagnose cancer
Researchers from the VUMC Cancer Center in Amsterdam have mastered a breakthrough technology that detects different types of cancer in a single bloodstream at an early stage.
Currently, we mainly detect cancer by scanning and tissue biopsy. These methods are very time-consuming, complicated and expensive. For example, CT scans can detect large tumors, but early tumors cannot be found. The method of detecting cancer by blood is called "liquid biopsy", and its greatest advantage is that cancer cells can be detected at an early stage.
Lead researcher Tom Würdinger and his team have found that platelets in the blood of cancer patients have special RNA markers that help us with DNA manipulation for specific tumors. The main role of platelets is to help the blood coagulate normally, but recent studies have shown that platelets also play an important role in cancer tumor growth and metastasis. Platelets in cancer patients contain specific markers of RNA that can help us distinguish between 96% of healthy individuals and patients with different types of cancer.
[2] JPCB: Can red peppers also treat cancer?
Capsaicin is a burning compound in peppers that is commonly used in creams to help relieve pain. Recently, studies have shown that high doses of capsaicin can help kill prostate cancer cells; now published in the international journal The Journal In a research paper on Physical Chemistry B, researchers from abroad have discovered new clues that may help explain why capsaicin can kill prostate cancer cells, and related research may help researchers develop new therapies for prostate cancer. .
Scientists reported that about 10 years ago, capsaicin can help kill prostate cancer cells in the body of mice, but it is harmless to healthy cells. By converting to a dose suitable for humans, it may be necessary for individuals to take a large number of peppers every day. And revealing the working mechanism of capsaicin can help scientists develop new drugs for the treatment of prostate cancer in the form of injections or tablets.
[3] Nature: Tumor suppressor protein drives malignant cancer
Recently, scientists from the University of Pennsylvania and other places have found that the growth of malignant tumors and the changes in gene activity of DNA sequences are often directly related to the mutant p53 protein. The results of the research are published in the internationally renowned journal Nature. Or to help develop new strategies for dealing with cancers that are difficult to treat.
TP53 is a frequently mutated gene in all human cancers that encodes a tumor suppressor protein called p53, which normally suppresses tumors by regulating the cycle of cell division, and p53 protein also maintains rapid cell growth and division. Complete the purpose of inhibiting cancer. When DNA is damaged, p53 produces a series of protective effects to repair cellular DNA damage. If the damage is too severe, it will cause cell death. The mutation of TP53 gene will destroy its normal function and cause the cells carrying the damaged DNA to continue. Split until it causes cancer to occur.
To understand how mutant p53 gain-of-function (GOF) works, the researchers investigated the function of tumor-derived cancer cell lines in patients with different types of p53 GOF replacement amino acids to observe these mutant forms of p53. Which positions will be incorporated into the cancer cell genome.
[4] Cell: Please note that all organisms can spread and spread!
Cancer cells are not contagious, which is a default known in biology. But this common sense has been broken on the east coast of North America, a deadly leukemia-like condition that has spread from Prince Edward Island in Canada to New York State. This may be caused by cancer cells that float freely in the water. Stephen Goff of Columbia University in the United States, described the widespread spread of this cancer as "in a state of super transfer, can spread to new animals." This study was published in this week's Cell magazine.
Cancer, as a result of accumulation of somatic mutations in the life cycle of an organism, is generally not transmitted or transmitted to other individuals, and is limited by immunological recognition and rejection based on polymorphic surface proteins, particularly in major histocompatibility complexes. (MHC) vertebrates. However, some tumors are caused by infections (such as viruses). Although these sources of infection can be infectious, tumors are still formed by transformation of somatic cells in infected individuals. It is known that in two cases, tumor cells themselves can spread naturally as infectious cells: canine infectious sexually transmitted diseases (CTVT) are transmitted by sexual contact, Tasmanian pouch facial tumor disease (DFTD) between individuals By spreading. In both cases, the tumors showed that the genotypes did not match their host - the tumor cells found in all affected animals were unique genotypes reflecting their original subject.
[5] Science headline: There have been cancer mutations in your skin.
According to a recent study published in Science, normal skin often exposed to ultraviolet light contains many potential pathogenic mutations, including at least six cancer-related genes. Researchers at the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute in the United Kingdom have studied cancer-free eyelid skin samples and found that hundreds of clonal cell populations are interspersed throughout normal tissues, and it is important that the cancer cells in such small pieces of skin tissue contain cancer. Mutation.
To find out how somatic mutations accumulate in normal tissues, the Department of Cancer, University of Cambridge Medical Research, led by Campbell and Philip Jones, took 234 biopsy samples from the orbital dermis tissue exposed to sunlight. These samples were from four healthy people between the ages of 55 and 73 who had removed some of the orbital tissue during eyelid cosmetic surgery.
Using techniques that capture rare mutations, the team sequenced 74 exons with skin and other cancer genes, as well as the entire genome of a living tissue sample. Part of the reason researchers chose to sample skin cells was evidence that cell clones containing the tumor suppressor p53 mutation in normal skin.
[6] Subverting the lifestyle of cancer origin or important influence
An article recently published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences states that our theory of the cause of cancer needs to be revised. This article believes that the origin of cancer was previously thought to be caused by mutations in some genes, and mutations in oncogenes led to the emergence of cancer cells and began to expand. However, the latest research suggests that in normal tissues, genetically altered cells are also subject to pressure selection by the population, so this selection pressure and mutation together determine the formation of cancer cells and tumors. The factors that contribute to this change in choice pressure are related to lifestyle and aging.
The latest theory of cancer formation suggests that in normal tissues, certain cells carry carcinogenic mutations, but in healthy individuals or tissues, the cells of these genetic mutations still work normally, and their carcinogenic nature has been normal. The cells are pressed. Until there are some accidental or inevitable factors, such as aging, smoking, drinking, etc., the cells of the carrier's oncogenes have changed their environment, and the cancer cells become more adaptive to themselves. At this time, the cancer cells begin to erupt. Even in normal tissues, there are still few cancer cells, but these cancer cells cannot compete to win normal cells, so their number is always lower than a certain value, but no tumor, but the environment is worse. Cancer cells are more adaptive than normal cells, and the number begins to increase and form cancer.
[7] Science: Cancer important enzyme complex structure
Recently, researchers from the Southwestern Medical Center of the United States have successfully analyzed the atomic structure of an enzyme complex that plays an important role in the development of many cancers, particularly blood cancers. The relevant research results are published in the international academic journal science.
This successfully resolved enzyme complex, called polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2), is a key regulator involved in human development and regulates gene expression by altering chromatin structure. As an enzyme complex, PRC2 is capable of modifying histone-constituting histones, leading to critical changes in chromatin structure, thereby silencing the expression of specific genes. Previous studies have found that abnormal expression of PRC2 is associated with the development of lymphoma, leukemia, brain tumors and other diseases.
The researchers said that over- or under-representation of PRC2 leads to a corresponding silencing or activation of the gene, which is not a good thing for cells. The results of this study reveal how normal levels of PRC2 maintain enzyme activity in cells and how Regulated. The researchers also pointed out that they found different ways in which PRC2 works, which is very helpful for us to understand the chemical basis of the disease and to develop treatments for the disease. Several small molecule drugs that inhibit PRC2 enzyme activity and are used to treat certain types of lymphoma have been developed.
[8] Nature studies prove that eating antioxidants can promote cancer metastasis
Researchers from the Children's Institute of the Southwestern Medical Center at the University of Texas in the United States conducted a study that found that cancer cells benefit more from antioxidants than normal cells. This finding increases the consumption of cancer patients. Concerns about antioxidants in the diet. (Bio Valley has previously reported that antioxidants accelerate the transfer of mouse skin cancer cells.)
Cancer cell metastasis is the process by which cancer cells travel from the primary site to other parts of the body and is an important cause of death in most cancer patients. The team found that anti-oxidant treatment of cancer mouse models caused cancer cells to spread faster. The relevant research results are published in the international academic journal Nature.
It has long been known that cancer cells travel from one site to the rest of the body. This is a very inefficient process, and most cancer cells that enter the bloodstream will not survive.
[9] Scientists reveal the process of most cancer origins
The p53 gene has been described as a "genomic guardian" because of its prominent role in preventing gene mutation. More than half of cancers are thought to be caused by p53 mutations or loss of function, and a recent study was explained by Dr. Richard Moran.
An article published in the journal Molecular Cancer Therapeutics shows that the p53 gene is mutated or loses the function of activating protein complexes called mammalian-targeted rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1). This helps regulate the energy resources needed for cell proliferation. mTORC1 consists of dozens of proteins that use the intracellular lysosomal membrane as a scaffold to bring all of these proteins together. For the needs of normal cells, the p53 gene helps maintain an appropriate level of protein, called the tuberous sclerosis complex 2 (TSC2) in lysosomes. When p53 function declines, the study found that the level of lysosomal TCS2 decreased, and a small protein RHEB would replace it. It is this accumulation of RHEB that activates mTORC1 and leads to abnormal cell proliferation control.
"We first discovered the process of causing cancer overgrowth when there is no p53. These protein interactions resemble a series of events that occur in an individual chain leading to cancer development," Moran said.
[10] Science: New research opens new avenues for cancer immunotherapy
Recently, scientists from the Dana Farber Cancer Institute in the United States published a new research progress in the famous international academic journal science. They turned the best "friends" of tumors in the immune system into their biggest "enemies." ". This discovery will provide important insights into cancer immunotherapy.
Harvey Cantor, author of the article, said: "Our findings provide a new strategy for cancer-based treatments based on the immune system. By targeting intracellular signaling pathways that limit the response of immune cells to cancer cells, we can turn them into cancer. Cell killers. How to develop antibodies and small molecule drugs that trigger this change is a challenge we still face."
When the body is in an infected or inflammatory state, effector T cells undergo rapid changes, they will arm themselves and divide into different groups to target specific disease cells. Regulatory T cells are another immune cell in the body that regulates effector T cells and prevents effector T cells from damaging normal tissues.
The inventory in 2015 is going on... Stay tuned!
Sharing is a virtue, then share it.
 Latest †activity: Fund project pre-deposit, content (recommended)
Latest †activity: Fund project pre-deposit, content (recommended)
 How to pay attention - pay attention to send notebook
How to pay attention - pay attention to send notebook
Search the public number "Rui Sai Bio" to choose to pay attention
The phone scans the QR code below to follow 
On the WeChat client, you can click on “Rui Sai Classroom†in the “Rice Race Activity†at the bottom to see more exciting information.
 Ruisai Bio R&S
Ruisai Bio R&S
There is fresh technology information here, and there are biological creatures here.
There is a scientific research sentiment here, and everything here is related to biology.
Oncology articles, department articles, experimental techniques, information sections
Submission email:
Salted Wakame Stalks
The original ecological Wakame means that we pack the young Wakame with saturated salt water directly after washing without any preservatives.Original ecological products are the favourite of housewives.
How to eat:
- Soaking about 30 minutes to moderate salty
- Cook . make salad or add to hot pot after draining the wate
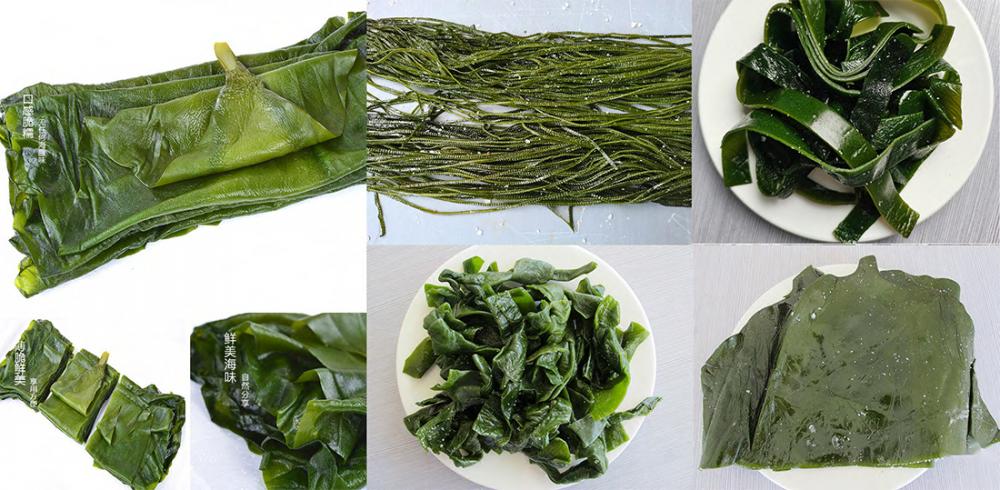

The difference between deep sea kelp and traditional ordinary kelp
Nutrational Effects
Salted Wakame Stalks,Salted Wakame,Natural Spirulina,Vegetables From The Sea
Shandong Haizhibao Ocean Science and Technology Co.,Ltd. , https://www.haizhibaoseafood.com